Supernova Rainbow
Supernova Rainbow: A Spectacular Display of Colors in the Sky
Have you ever imagined witnessing a breathtaking combination of a spring shower and a nearby supernova? While such a sight is purely hypothetical, it's fascinating to delve into the world of atmospheric optics and explore the concept of a "Supernova Rainbow." In this article, we will dive deeper into the phenomenon, providing a more detailed understanding of its formation and appearance.
When raindrops interact with sunlight, they give rise to the beautiful natural phenomenon we know as a rainbow. However, the appearance of a rainbow can vary depending on several factors, such as the size of the raindrops and the angle at which sunlight interacts with them. In the case of a Supernova Rainbow, we focus on two distinct slices of the rainbow to gain a comprehensive understanding of its unique characteristics.
The lower slice of the rainbow is formed when sunlight passes through small raindrops, causing the light to scatter and disperse. As a result, the colors appear slightly washed out, and within the main bow, we can observe 3-4 faint supernumerary bows. These additional bows are created through the interference between light waves, producing a mesmerizing effect.
In contrast, the upper slice of the Supernova Rainbow showcases an entirely different perspective. Imagine witnessing a rain shower illuminated by a distant point source of light, such as the dazzling diamond ring of a solar eclipse or even a nearby supernova explosion. Without the blurring effect caused by divergent light beams, the hues within the rainbow intensify significantly. As a result, we are treated to a vivid and vibrant array of sharp supernumerary interference fringes.
To gain further insights into the formation and characteristics of a Supernova Rainbow, scientists have conducted simulations using different raindrop sizes. These simulations reveal that raindrops with an average diameter of 0.7mm, and a standard deviation of 8%, produce the most accurate representation of this captivating atmospheric phenomenon. The calculations involved in these simulations utilize Airy theory scattering, employing a modified version of IRIS software.
In summary, a Supernova Rainbow presents a truly remarkable spectacle in the sky. By exploring the lower and upper slices of the rainbow, we can observe the subtle differences in color intensity and the presence of supernumerary bows. This phenomenon serves as a testament to the intricate interactions between light, raindrops, and various celestial events.
Key Points:
- A Supernova Rainbow is a hypothetical combination of a spring shower and a nearby supernova explosion.
- The lower slice of the rainbow appears slightly washed out due to light scattering by small raindrops.
- Within the main bow, we can observe 3-4 faint supernumerary bows created by interference between light waves.
- The upper slice of the Supernova Rainbow is more vibrant and intense, visible when rain is illuminated by a distant point source of light.
- Simulations using different raindrop sizes reveal that an average diameter of 0.7mm with a standard deviation of 8% produces the most accurate representation.
- Airy theory scattering calculations, using a modified version of IRIS software, are employed to study the formation and characteristics of a Supernova Rainbow.
In conclusion, while witnessing a Supernova Rainbow may be purely speculative, understanding its formation and intricacies allows us to appreciate the wonders of atmospheric optics. Exploring the interplay between raindrops, sunlight, and celestial events not only broadens our scientific knowledge but also enhances our appreciation for the natural beauty that surrounds us. So, next time you spot a rainbow in the sky, take a moment to marvel at the captivating phenomenon that is a Supernova Rainbow.
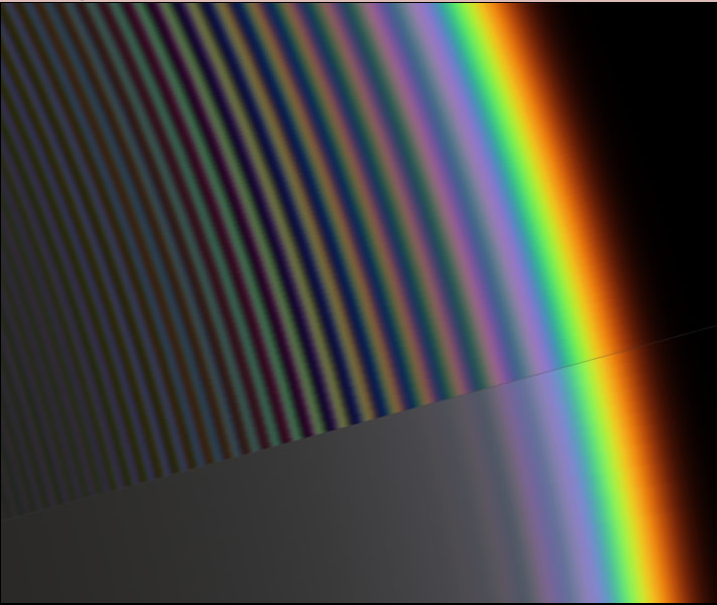
Sometimes we might wish for a Spring shower plus a nearby supernova
The lower slice of rainbow is how it appears from small raindrops and light smeared out by the divergent rays from the sun’s 0.5° diameter disk. The colours are slightly washed out and inside the main bow there are 3-4 weak supernumerary bows produced by interference between light waves.
The upper slice is how we would see the bow from a rain shower lit by a distant point source of light, perhaps the diamond ring of a solar eclipse or a nearby supernova explosion. Without the blurring by divergent light beams the hues intensify and we see a deep and colourful array of sharp supernumerary interference fringes.
Simulations for a range of raindrop sizes - mean diameter 0.7mm with a std. deviation of 8%. Airy theory scattering calculations using a modified version of IRIS software.
©Les Cowley
Note: this article has been automatically converted from the old site and may not appear as intended. You can find the original article here.
Reference Atmospheric Optics
If you use any of the definitions, information, or data presented on Atmospheric Optics, please copy the link or reference below to properly credit us as the reference source. Thank you!
-
<a href="https://atoptics.co.uk/blog/supernova-rainbow/">Supernova Rainbow</a>
-
"Supernova Rainbow". Atmospheric Optics. Accessed on December 4, 2024. https://atoptics.co.uk/blog/supernova-rainbow/.
-
"Supernova Rainbow". Atmospheric Optics, https://atoptics.co.uk/blog/supernova-rainbow/. Accessed 4 December, 2024
-
Supernova Rainbow. Atmospheric Optics. Retrieved from https://atoptics.co.uk/blog/supernova-rainbow/.