Autumnal Fogbow Finland - OPOD
Autumnal Fogbow Finland - OPOD: A Captivating Atmospheric Phenomenon
Autumn in Finland brings with it a magical display of atmospheric optics, showcasing the ethereal beauty of nature. Among these captivating phenomena is the Autumnal Fogbow, a rare sight that leaves observers in awe. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of the Fogbow and explore its formation, characteristics, and the scientific principles that make it such a mesmerizing spectacle.
Unveiling the Secrets of the Autumnal Fogbow
The formation of a Fogbow closely resembles that of a rainbow, where light is refracted, reflected, and dispersed through water droplets suspended in the air. However, there are distinct differences that set the Fogbow apart. While rainbows are formed by larger raindrops, Fogbows arise from much smaller droplets, typically ranging from 10 to 100 microns in diameter. This size disparity gives the Fogbow its characteristic diffuse appearance.
The Role of Waves in Fogbow Formation
In a Fogbow, waves play a crucial role in the creation of its unique visual structure. Similar to rainbows, waves reflect off the opposite face of the water droplets. However, due to the small size of the droplets, the waves overlap and interfere with each other, resulting in a broad and hazy bow rather than a distinct band of colors. This overlapping effect gives the Fogbow its enchanting allure.
The Enigmatic Heiligenschein
Accompanying the Fogbow in Finland's autumn mornings is another captivating phenomenon known as heiligenschein. This optical effect manifests as a bright glow surrounding the shadow of one's head when cast on dew-wetted grass. The heiligenschein is created when sunlight passes through dew drops on grass blades and is subsequently scattered backward towards our eyes.
The Intricacies of Dew Drops
Dew drops play a vital role in the formation of heiligenschein. As the sun's rays pass through these tiny droplets, they act as lenses, focusing the light onto the surfaces of nearby leaves. The scattered light then travels back through the droplets and reaches our eyes, creating the luminous halo effect. Although wave diffraction also occurs in this phenomenon, its effects are not readily noticeable to the naked eye.
Unraveling the Autumnal Fogbow's Mystery
The Autumnal Fogbow in Finland is a captivating natural spectacle that showcases the intricacies of atmospheric optics. While its formation resembles that of a rainbow, the use of smaller water droplets and the interference of waves give the Fogbow its distinctive diffuse appearance. Paired with the enigmatic heiligenschein, created by sunlight passing through dew drops on grass, this phenomenon offers a visual feast for those fortunate enough to witness it.
Tips for Observing the Autumnal Fogbow
If you find yourself in Finland during autumn and wish to catch a glimpse of the mesmerizing Fogbow, here are some tips to enhance your chances:
-
Choose Foggy Mornings: Foggy conditions provide the ideal backdrop for Fogbow formation. Head out early in the morning when the mist is at its peak to increase your chances of witnessing this phenomenon.
-
Open Spaces: Seek out open areas such as fields or meadows where the fog can disperse and allow for better visibility of the Fogbow.
-
Look Away from the Sun: Unlike rainbows that form opposite the sun, Fogbows can be observed in the direction of the sun. Look away from the sun to spot this ethereal display.
-
Use Polarized Sunglasses: Polarized sunglasses can help reduce glare and enhance contrast, making it easier to observe and appreciate the delicate hues of the Fogbow.
In Conclusion
The Autumnal Fogbow in Finland is a captivating atmospheric phenomenon that mesmerizes observers with its diffuse and hazy appearance. Created by smaller water droplets and the interference of waves, the Fogbow stands apart from its rainbow counterpart. Accompanied by the heiligenschein, which adds an enchanting glow to dew-wetted grass, this phenomenon showcases the fascinating interplay of light, water, and atmospheric conditions. So, if you find yourself in Finland during autumn, keep your eyes peeled for this awe-inspiring display of nature's beauty.

Mists and mellow fruitfulness
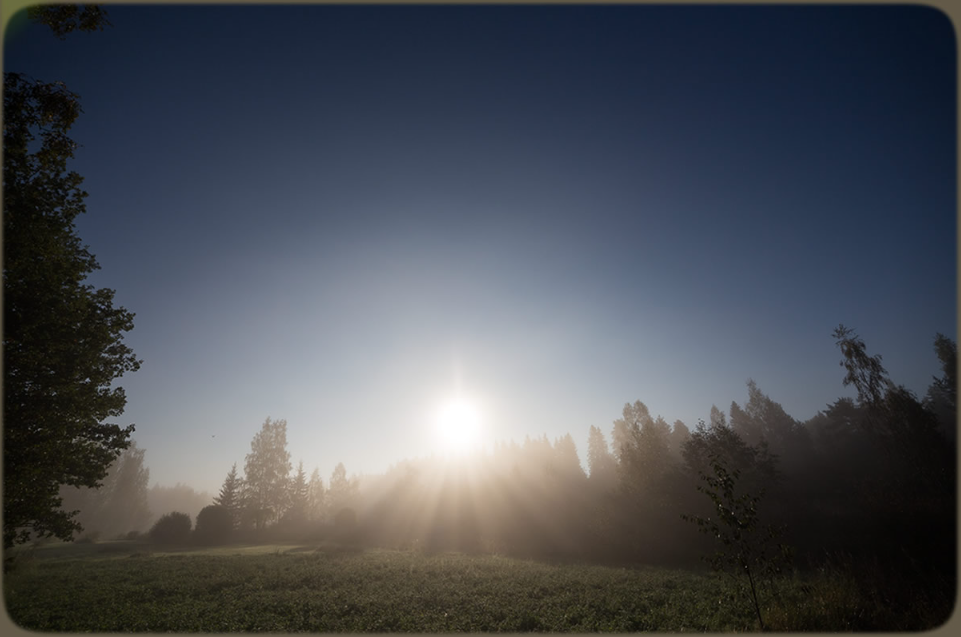
Fogbow and heiligenschein by Jari Luomanen (Atmospheric Phenomena) on an Autumnal Finland morn.
©Jari Luomanen, shown with permission
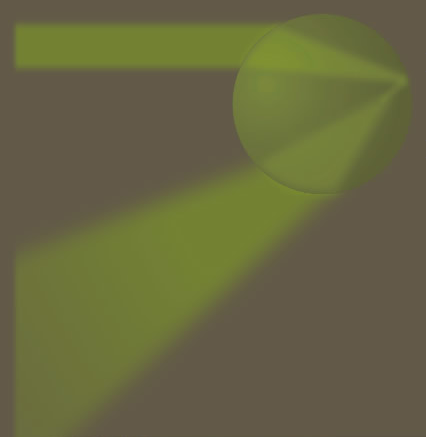

Waves dominate fogbow formation. As in a rainbow they reflect off the drop's opposite face. But unlike a rainbow the drop is small (10-100 micron dia.) and the waves overlap and interfere to produce a broad and diffuse bow.
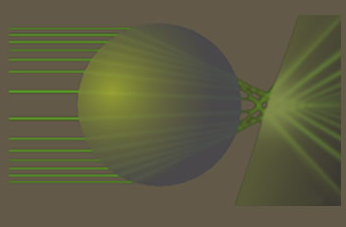
Rays are our own construct and an approximation but they are enough to describe the heiligenschein, the bright glow around the head's shadow when cast on dew wetted grass.
The dew drops focus the sun's light onto leaf surfaces where it is scattered backwards through the drop towards our eyes.
Wave diffraction is there too but its effects are not noticeable.

Note: this article has been automatically converted from the old site and may not appear as intended. You can find the original article here.
Reference Atmospheric Optics
If you use any of the definitions, information, or data presented on Atmospheric Optics, please copy the link or reference below to properly credit us as the reference source. Thank you!
-
<a href="https://atoptics.co.uk/blog/autumnal-fogbow-finland-opod/">Autumnal Fogbow Finland - OPOD</a>
-
"Autumnal Fogbow Finland - OPOD". Atmospheric Optics. Accessed on November 26, 2024. https://atoptics.co.uk/blog/autumnal-fogbow-finland-opod/.
-
"Autumnal Fogbow Finland - OPOD". Atmospheric Optics, https://atoptics.co.uk/blog/autumnal-fogbow-finland-opod/. Accessed 26 November, 2024
-
Autumnal Fogbow Finland - OPOD. Atmospheric Optics. Retrieved from https://atoptics.co.uk/blog/autumnal-fogbow-finland-opod/.