OPOD - Arctic Fogbow
OPOD - Arctic Fogbow: A Captivating Natural Phenomenon
Have you ever heard of an Arctic Fogbow? This mesmerizing atmospheric optical phenomenon is a captivating sight to behold. Unlike a traditional rainbow, which forms from raindrops, a fogbow is created by the scattering of light from minuscule fog droplets. In this article, we will delve deeper into the enchanting world of Arctic Fogbows and explore the intricacies of their formation.
When sunlight filters through a fog layer near the cold ice and sea, the fog droplets scatter the light in all directions. This scattering phenomenon is not limited to simple refraction or reflection but involves the diffraction and oscillation of light waves. As a result, a complex ringed pattern emerges in the sky, surrounding the observer.
The Arctic Fogbow's beauty lies in its delicate hues. The sunlight passing through the fog layer creates a soft, pastel color palette. Along the outer edge of the fogbow, one can witness subtle shades of red, while hints of blue grace its inner part. These ethereal colors add to the mystique and allure of this natural spectacle.
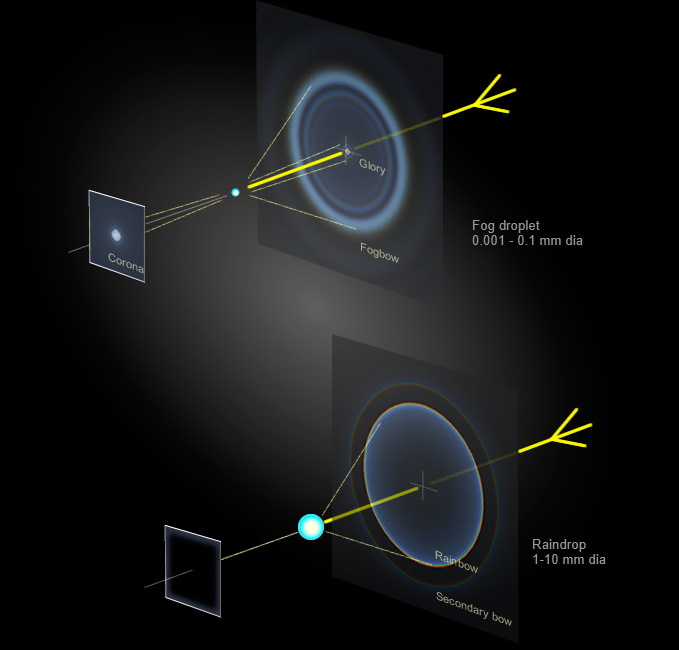
It is important to note that the finite size of the sun and variations in droplet size contribute to blurring out the finest details of the fogbow's structure. Additionally, the background skylight obscures most of the pattern, allowing only the brightest parts to be visible. These include a colored corona around the sun, a ringed glory directly opposite, and a large and ghostly fogbow.
Interestingly, fog droplets are significantly smaller than raindrops. While raindrops measure between 10 and 1000 times larger than fog droplets, their size difference leads to variations in their diffraction effects. Consequently, when raindrops are involved in the formation of an optical phenomenon, such as a rainbow, the resulting effect is a sharp and distinct rainbow, rather than a diffuse fogbow.
In the case of the Arctic Fogbow, its softer and more diffuse appearance can be attributed to the smaller size of the fog droplets. These tiny droplets allow for greater diffraction, resulting in a broad and hazy fogbow that seems to accompany the observer as they navigate through the fog.
The Arctic region provides a unique setting for observing these captivating atmospheric optics. Imagine being on a Russian nuclear-powered icebreaker, sailing through the icy expanse of the North Pole, and witnessing the ethereal beauty of an Arctic Fogbow. The combination of the frozen landscape, the sea, and the soft sunlight filtering through the fog creates a truly enchanting experience.
In conclusion, the Arctic Fogbow is a stunning natural phenomenon that showcases the interplay between light and fog droplets. Its delicate hues, complex patterns, and diffuse appearance make it a captivating sight to behold. Whether observed from the deck of an icebreaker or in other Arctic settings, this ethereal display of nature's beauty never fails to leave observers in awe.

Arctic Fogbow at latitude 82.5N seen from a Russian nuclear powered ice-breaker. Photographer Paul Money (Astrospace) was on a visit to the North Pole. ©Paul Money, shown with permission.
Soft sunlight filters through a fog layer near the cold ice and sea. The miniscule fog droplets scatter light to form a broad fogbow that accompanies the ship as it forces through the ice. Pastel reds fringe the bow'souter edge with the merest hints of blues at the inner.
Fog droplets are small enough that when light interacts with them its wave nature is significant. Light is not simply refracted or reflected at the drop surface. Instead, its waves are scattered, diffracted, in all directions to produce a wildly oscillating and complex ringed pattern all around the sky.
The finite size of the sun and variations in droplet size blur out the finest structure and the background skylight obscures all but the pattern's brightest parts; a coloured corona around the sun, a ringed glory directly opposite and a large and ghostly fogbow.
Raindrops are 10-1000X larger than fog droplets and their diffraction effects are consequently small.. The corona and glory shrink to insignificance and instead of a diffuse fogbow we see a sharp rainbow.
Note: this article has been automatically converted from the old site and may not appear as intended. You can find the original article here.
Reference Atmospheric Optics
If you use any of the definitions, information, or data presented on Atmospheric Optics, please copy the link or reference below to properly credit us as the reference source. Thank you!
-
<a href="https://atoptics.co.uk/blog/opod-arctic-fogbow/">OPOD - Arctic Fogbow</a>
-
"OPOD - Arctic Fogbow". Atmospheric Optics. Accessed on April 18, 2024. https://atoptics.co.uk/blog/opod-arctic-fogbow/.
-
"OPOD - Arctic Fogbow". Atmospheric Optics, https://atoptics.co.uk/blog/opod-arctic-fogbow/. Accessed 18 April, 2024
-
OPOD - Arctic Fogbow. Atmospheric Optics. Retrieved from https://atoptics.co.uk/blog/opod-arctic-fogbow/.